An Essential Requirement
Digitalisation requires telecommunications systems to evolve in order to provide the connectivity needed to meet the increasingly demanding requirements of digital applications connected both to the Cloud and to connected objects (IoT), which are now necessary to ensure company operations.
The increasing requirements for communication and interconnections between mobile users have also lead to the introduction of new architectures, protocols and technologies to optimise workflows.
The corporate network is the backbone of global performance, so it is essential to work with a partner who can guarantee
- Permanent and secure connectivity
- Seamless resilience
- Maximum application performance
- Quality support and assistance
Robust Hybrid Networks
Sonema’s team of experts will advise you on the best technological strategies to meet your business challenges. Our one-stop-shop approach enables us to deliver the most suitable, secure and customised connectivity and cloud access services to help you improve efficiency and productivity
Working with our network of partners, Sonema guarantees you complete control of the solutions we implement in addition to providing fine-tuned management of your networks to ensure optimum availability and usage of all your services, tools and applications.
Sonema is committed to the quality of service and continuous availability of your networks. Each and every company and administration, must have access to high-performance and scalable infrastructures.
Benefits
Maximum Resiliency
- Alternative transmission paths via automated failover
- Up to 100% availability
Enhanced Performance
- Better user experience
- Dynamic bandwidth allocation
- Anticipation and management of network congestion
Better Cost Management
- Improved operating costs
- Optimisation of traffic flows between remote sites
Discover Our Connectivity Services
SD-WAN
A fully managed service for the active and optimised management of your hybrid networks.
Premium Internet Services
Dedicated Internet access for a reliable and high performance terrestrial connection.

Terrestrial MPLS
Dedicated, secure, high-performance terrestrial connectivity.

Satellite Links
Rapid, easy to install corporate VSAT links. iDirect, Vipersat and SCPC/FDMA solutions available.

Star Lite Ka-Band
Get reliable, cost-effective and competitive broadband connectivity in Africa.

LAN Management
Improve the performance of your local area networks by allowing us to monitor your devices.
ExpressRoute Sonema
Your private connection to the Microsoft Azure and Office 365 services.

Visio
A tailor-made range of securely integrated and optimised videoconferencing equipment for your network.

Network Booster
Guaranteed optimal network performance in all conditions through optimisation, monitoring and load balancing of your circuits.

Skyview
A secure customised Web-based interface to view your network performance and quality of service.
Star Lite
A secure and scalable high-quality high-speed asymmetrical Internet connection to meet your Internet requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the components of a Satellite IP network?
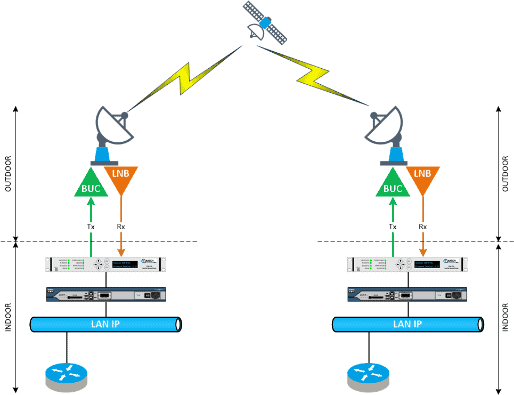
A commercial geostationary satellite communications network (36,000 km orbit at the equator) consists of one or more satellites and several earth stations, in point-to-point, star or mesh topology.
Satellites act as repeaters between earth stations, which may or may not incorporate a central hub, depending on the topology and use of the network (intranet, internet). Satellites can provide C-band (3 – 8 GHz, hemispheric coverage), Ku-band (12 – 18 GHz, regional coverage) or Ka-band (26 – 40 GHz, zonal coverage, e.g. one country) coverage.
Earth stations consist of an outdoor section, incorporating a parabolic antenna with a diameter that varies between 0.5 and 4.5 metres depending on the frequency band and the performance required, and which can be more than 20 metres in diameter in the case of a teleport. The rest of the outdoor section is an RF chain consisting of a transmit amplifier, usually a BUC, and a receive amplifier, usually an LNB.
The indoor portion of an earth station is composed of equipment specific to satellite telecommunications (hubs, modems, demodulators) and IP equipment for connection to the LAN (routers, switches, firewalls).
Are there any specificities related to land connectivity in Africa?
Additionally, infrastructure problems such as power supply, theft and vandalism of fibre networks and bad weather are also specific features to be taken into account, as is the geopolitical instability that affects many African countries. All of these points, coupled with complex and uncoordinated regulatory conditions, explain the price and quality discrepancies of terrestrial connectivity between African countries and the frequent need to maintain satellite connectivity.
Are there different types of terrestrial Internet access and what are the differences between them?
What is a local breakout?
What are satellite communication services used for?
What does VSAT mean?
How secure are satellite communications?
Are satellite services and equipment reliable?
Are satellite services and equipment scalable?
Why are satellites an essential component when designing a telecommunications network?
Satellite-based wireless systems allow for rapid deployment and/or restoration of communications in areas where terrestrial infrastructure may be insufficient or unreliable, particularly on the African continent to prevent problems that may arise with terrestrial connectivity: outages due to geopolitical or climatic problems, infrastructure theft and vandalism or complex and uncoordinated regulatory conditions between countries.
IT management should integrate satellite services and networks as a redundancy requirement into their own network or communication architecture. These systems should be brought to the forefront and included early in the planning process. Satellite services enable the implementation of communications services in a matter of days, proving their value in providing “instant infrastructures” for commercial, government and emergency communications.
Why are satellites an essential component when it comes to data backup policies?
What is the difference between a LEO, MEO and GEO satellite?
MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) Intermediate orbit between low earth and geostationary orbit. MEO satellites operate at an altitude of between 5,000 and 20,000 km. HTS MEO constellations have been deployed to provide low latency and high bandwidth connectivity. As LEO & MEO satellites are mobile, they impose propagation (doppler effect) and handover (switchover) constraints in contradiction with current multimedia needs (high data rates, quality of service).
GEO (Geostationary Earth Orbit) is used for telecommunications and live television broadcasting. These satellites orbit along a circular path, within the plane of the equator and their radius is 42 164 km from the centre of the earth at an altitude of 35 786 km above the earth’s surface. From the ground, geostationary satellites appear to be stationary which is where the name comes from.
LEO satellites provide lower latency, but as they are not geostationary, they require the installation of a satellite to follow their trajectory.
What types of network architecture are available?
What are the benefits of a hybrid network?
It supplies additional throughput for terrestrial links by providing a communal pool of satellite bandwidth for different agencies from a satellite network to avoid congestion when various links are overloaded.
It reduces global connectivity costs by optimising connection use between remote sites.
What is a hybrid network?
What does MPLS mean?
What does network oversubscription mean?
- An oversubscription ratio of 1:1 means that the bandwidth is guaranteed
- An oversubscription ratio of 1:8 means that 8 users share the bandwidth
A Broadband Internet access is usually a service with non-guaranteed bandwidth whereas a dedicated Internet access (DIA) guarantees bandwidth from the customer’s facilities to the public Internet.
What is SD-WAN?
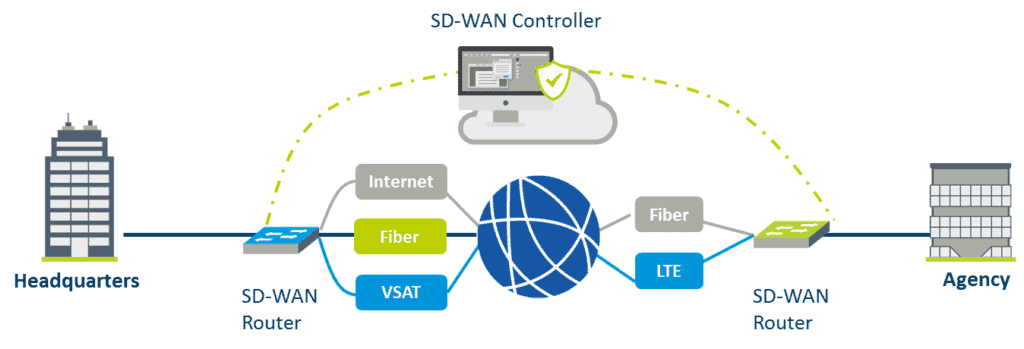 SD-WAN stands for Software Defined Wan (WAN or Wide Area Network). There is no standard definition for SD-WAN within the industry. SD-WAN technology is used within the framework of hybrid networks (MPLS or VSAT) and uses WAN functions such as VPN, WAN optimisation, IPsec tunnel mode, hybrid WAN, deep packet inspection, rule management and analysis and assessment services. The purpose of SD-WAN is to simplify the management and operation of WAN by identification applications and dynamic path selection for traffic.
SD-WAN stands for Software Defined Wan (WAN or Wide Area Network). There is no standard definition for SD-WAN within the industry. SD-WAN technology is used within the framework of hybrid networks (MPLS or VSAT) and uses WAN functions such as VPN, WAN optimisation, IPsec tunnel mode, hybrid WAN, deep packet inspection, rule management and analysis and assessment services. The purpose of SD-WAN is to simplify the management and operation of WAN by identification applications and dynamic path selection for traffic.
Sonema’s SD-WAN offer is an entirely managed service, backed up by stringent SLAs which allows us to improve the customer’s hybrid network performance through the use of routing, security and optimisation rules.
How does terrestrial connectivity transit between Europe and Africa?
Is it possible to optimise a network without increasing the bandwidth?
Would you like to know more?
Contact us on +377 93 15 93 15 or by clicking here